Conveyor belts are often constructed from a rubber or plastic compound along with one or more layers of fabric or steel cables with various widths. Polyvinyl chloride, fabric-like polyester or styrene-butadiene rubber, and many layers of polyester or nylon fabric can all be used to make conveyor belts. Read More…
For more than 60 years, we have been offering innovative conveyor belting to customers worldwide. Our full line of products include perforated belts, vacuum belts, nylon core belts, and plastic modular belting. We have grown our reputation based on providing outstanding customer service as well as conveyor belt materials that will provide long-lasting value. For more information on how we may be...

At Shipp Belting, we specialize in manufacturing and distributing high-quality conveyor belts designed to meet the diverse needs of industrial operations. With decades of experience behind us, we’ve built our reputation on reliability, technical expertise, and a deep understanding of how material handling impacts overall efficiency.

At Mol Belting Systems, we specialize in providing high-quality conveyor belts designed to meet the diverse needs of industries worldwide. Our product range includes an extensive variety of conveyor solutions, such as modular plastic belts, polyurethane, and rubber conveyor systems, all engineered for efficiency, durability, and superior performance.

We have a wide range of products that allow us to find the right solutions for all our customer’s material handling needs. We provide conveyor belts made out of variety of materials. Our research and development department works hard to ensure that we are bringing our customers products that are on the leading edge of innovations at all times. For more information on how we may be able to...

More Conveyor Belt Materials Manufacturers
Comprehensive Guide to Conveyor Belt Materials: Types, Applications, and Selection Tips
Choosing the right conveyor belt material is essential for maximized efficiency and safety in industrial automation, manufacturing, food processing, mining, logistics, and countless other sectors. The most commonly used substance for conveyor belts is rubber composite, celebrated for its adaptability, durability, smooth operation, and seamless construction. Its lack of gaps or openings helps minimize product loss and contamination, making it especially valuable for demanding and hygienic environments.
To enhance strength, flexibility, and performance, many conveyor belt materials incorporate reinforcements such as cloth, steel, polyester, nylon, or fiberglass. In reality, most modern flat belts are engineered with a specialized core material and protective covering, ensuring optimal performance in specific industrial applications. Understanding the properties, strengths, and best-use scenarios for each conveyor belt material type is critical for system designers, engineers, facility managers, and procurement teams.
Looking for the best conveyor belt solution for your business? Explore the following sections to learn how to choose the ideal belt material for your industry, operational requirements, and budget.

What Are the Main Types of Conveyor Belts and Their Materials?
Different conveyor belt materials are engineered to meet the diverse demands of various conveyor systems. These systems include troughed conveyors, inclined conveyors, horizontal conveyors, food-grade conveyors, and overhead conveyors. However, it’s important to note that belt conveyors are distinct from chain conveyors, pneumatic conveyors, and screw conveyors, which utilize different mechanisms for material movement.
One of the most crucial considerations when designing or upgrading a conveyor system is selecting the correct belting material. The wrong choice can lead to increased downtime, reduced productivity, product contamination, higher maintenance costs, or even safety hazards for workers.
- Rubber Conveyor Belts – Ideal for heavy-duty, impact-resistant, and high-grip applications.
- Thermoplastic Conveyor Belts – Known for chemical resistance, easy cleaning, and versatility in food and pharmaceutical industries.
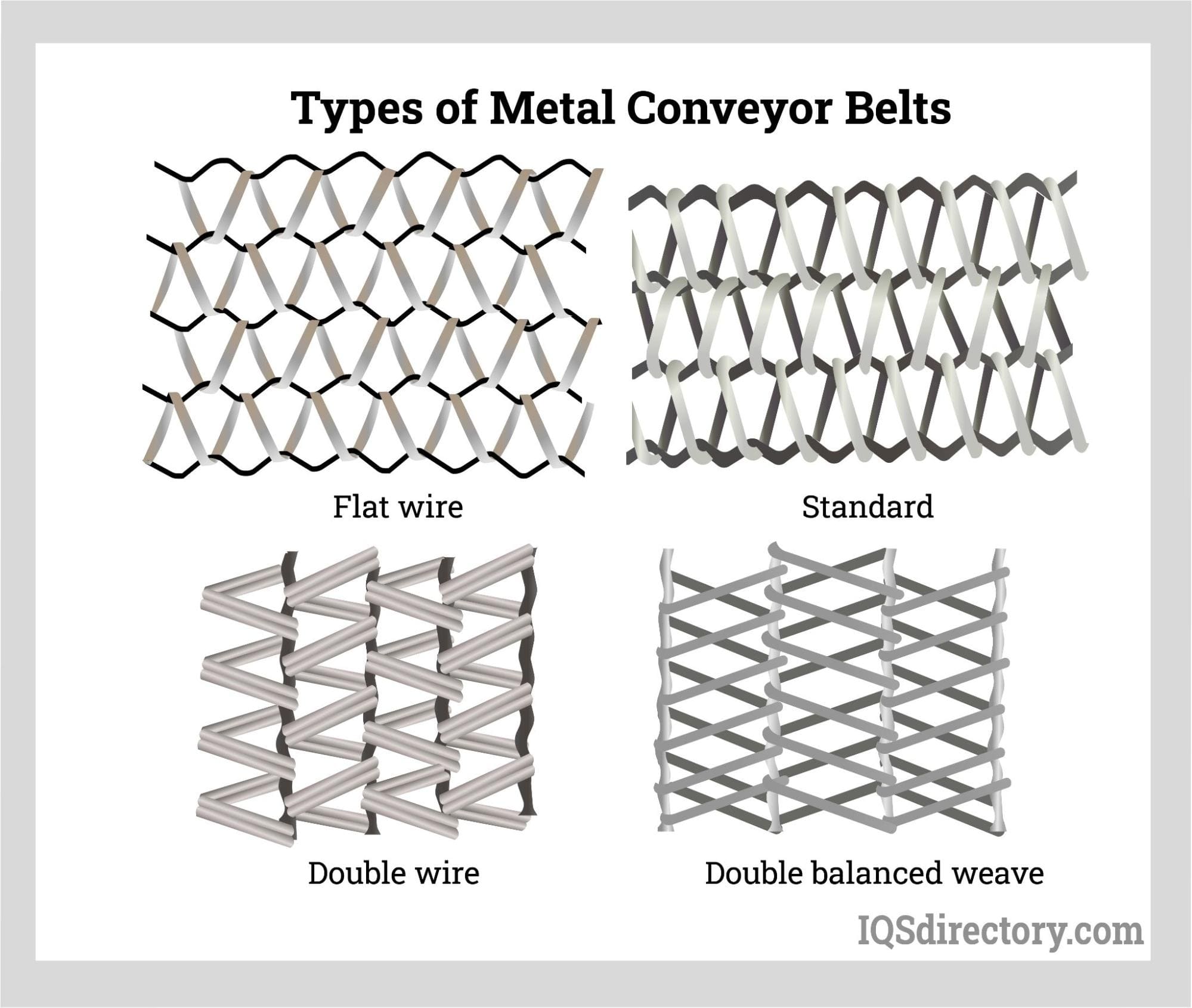
- Metal Conveyor Belts – Preferred in high-temperature, abrasive, or hygienic processes.
- Fabric Conveyor Belts – Cost-effective and suitable for light- to medium-duty bulk material handling.
- Modular Plastic Conveyor Belts – Popular in food processing and packaging due to their hygiene and flexibility.
- Specialty Belts – For unique applications such as heat resistance, oil resistance, anti-static, and flame-retardant requirements.
Thermoplastic Conveyor Belt Material: Properties, Benefits, and Applications
Thermoplastic conveyor belt materials, primarily made from polyurethanes and other polymeric compounds, offer exceptional performance characteristics for a wide range of industries. Polyurethanes are synthesized by combining diisocyanates (TDI and MDI) with polyols, resulting in hundreds of material variants tailored for specific applications.
Through advanced materials engineering, manufacturers can fine-tune the mechanical properties of polyurethane—including flexibility, load capacity, abrasion resistance, and recovery—enabling solutions for highly specialized needs. These belts are especially prized for applications requiring:
- High load-bearing capability in tension and compression, making them suitable for heavy-duty conveyors and impact zones.
- Outstanding flex fatigue resistance, allowing them to perform reliably in applications with repeated bending and flexing, such as packaging lines or sorting facilities.
- Excellent elongation and recovery, ensuring dimensional stability and minimal belt stretch even under varying loads.
- Consistent material properties in challenging environments, including exposure to water, oil, grease, and a wide range of chemicals. Polyether-based polyurethane compounds are especially valued for their longevity in underwater or wet applications.
- Superior electrical insulation, making them safe for use around sensitive electronics or in automated assembly.
Industries that benefit most from thermoplastic conveyor belts include food processing, pharmaceuticals, electronics manufacturing, packaging, and logistics. Their smooth, non-porous surfaces are easy to clean and sanitize, meeting stringent hygiene standards. Additionally, the ability to customize hardness and surface texture makes them suitable for transporting delicate items or products that require gentle handling.

Key Questions: Is a Thermoplastic Conveyor Belt Right for My Operation?
- Are you searching for conveyor belts with chemical or moisture resistance?
- Does your facility require easy-to-clean, food-grade conveyor belts?
- Do you need a belt that withstands repeated flexing or high impact?
- Would a customizable belt surface or hardness improve your process?
- Are you looking for longer belt lifespan and reduced maintenance downtime?
If you answered yes to any of these, a thermoplastic conveyor belt may be your best choice. Contact a conveyor belt supplier for expert guidance on thermoplastic belt options.
Metal Conveyor Belt Material: Durability, Hygiene, and Specialized Uses
Metal conveyor belts are renowned for their robustness, longevity, and suitability for demanding environments. These belts—typically made from stainless steel, carbon steel, or formed aluminum—offer a unique combination of properties that make them indispensable in certain industries:
- High tensile strength and rigidity, ensuring that belt shape and performance remain consistent over long service intervals, even under heavy loads.
- Extreme resistance to abrasion and harsh chemicals, making them ideal for conveying sharp, abrasive, or corrosive materials.
- Excellent temperature tolerance, allowing for use in baking, drying, heat-treating, freezing, or other thermal processing environments.
- Open mesh or perforated designs, enabling drainage, airflow, or rapid cooling—critical for some food processing and metalworking applications.
- Easy cleaning and sanitation, supporting strict hygiene standards in food, beverage, and pharmaceutical production.
Common applications for metal conveyor belts include:
- Food processing lines (especially for bakery, meat, poultry, seafood, and snack foods)
- Automotive parts manufacturing
- Electronics assembly and curing ovens
- Glass, ceramic, or brick production
- Pharmaceuticals and medical devices
- Bulk material handling and recycling
While metal belts are exceptionally durable and flat, they are less flexible and more difficult to shape than their fabric or thermoplastic counterparts. This can limit conveyor routing options but pays dividends in environments where belt integrity is paramount.

Ask Yourself: When Should You Consider Metal Conveyor Belts?
- Do you need a conveyor system that operates reliably at high temperatures?
- Is hygiene and easy cleaning a top priority in your process?
- Are you conveying sharp, abrasive, or corrosive materials?
- Would an open mesh belt improve cooling or drainage?
If so, metal conveyor belts could deliver the durability and process advantages your application demands. Request a quote from a metal conveyor belt supplier to learn more.
Fabric Conveyor Belt Material: Cost-Effective Solutions for Bulk Handling
Fabric conveyor belts are among the most widely used solutions for light- and medium-duty applications. These belts are typically constructed with layers of fabric (such as nylon, polyester, cotton, or wool) and a protective rubber or PVC cover.
Advantages of fabric belt materials include:
- Affordability – Lower material and manufacturing costs make them attractive for bulk commodity transport and general industry use.
- Medium impact resistance – Suitable for transporting gravel, sand, agricultural products, packaged goods, and other moderate-weight items.
- Flexibility and quiet operation – Particularly beneficial in environments where noise reduction is desirable, such as retail checkout lanes or parcel handling.
- Breathability – Natural fabrics allow air movement, which can reduce product sticking or spoilage.
Fabric belts are often specified in these sectors:
- Mining and quarrying
- Food and beverage
- Retail and logistics
- Agricultural processing
- Parcel and postal facilities
Nylon: Exceptional strength, heat resistance, and impact resilience. Nylon blends adhere well to rubber and exhibit lower mildew susceptibility than many other fabrics, making them reliable in humid or wet environments.
Polyester: Similar in many respects to nylon, polyester belts are valued for their cost-effectiveness and quietness in operation. They are commonly used where static build-up or noise reduction is important.
Natural fabrics (cotton, wool): These materials are selected for their breathability and gentle handling of sensitive or delicate products.

Fabric vs. Rubber Conveyor Belts: Which Is Better for Your Material Handling Needs?
- Is cost efficiency your top priority?
- Do you need a flexible, lightweight conveyor belt for bulk material transport?
- Are you handling packaged or moderately abrasive goods?
- Does your application require minimal noise and vibration?
If you answered yes to these, a fabric conveyor belt may be the best fit. Connect with fabric conveyor belt suppliers for expert recommendations and custom options.
Rubber Conveyor Belt Material: Strength, Versatility, and Industrial Applications
The rubber conveyor belt is the backbone of heavy industry, mining, aggregate, recycling, and many other sectors that demand superior durability and impact resistance. The continuous, flexible band efficiently moves products, bulk materials, or components from one point to another, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted workflow.
Rubber conveyor belts are manufactured from premium rubber compounds such as SBR, nitrile, EPDM, and neoprene, often reinforced with layers of fabric (nylon, polyester, cotton) or steel cords for added strength. Some advanced rubber belts incorporate leather, urethane, or PVC covers for enhanced performance in specialized applications.
- High resistance to abrasion, impact, and wear – Essential for transporting rocks, ores, minerals, and other coarse materials.
- Excellent load-carrying capacity – Capable of supporting heavy or bulky items over long distances.
- Versatility – Available in flat, cleated, sidewall, and endless-loop designs to accommodate various operational needs.
- Compatibility with a wide range of environments – Suitable for both indoor and outdoor use, with options for oil resistance, flame retardancy, and anti-static properties.
Nylon, a high-strength synthetic polymer, is frequently used to reinforce rubber conveyor belts. Its silk-like thermoplastic properties, high tensile strength, and resistance to abrasion and chemicals make it invaluable for industrial conveyor systems. By blending nylon with other additives, manufacturers tailor belt properties to specific operational challenges, such as high-impact loading or exposure to harsh conditions.

Top Considerations: Why Choose Rubber Conveyor Belts?
- Are you moving heavy, sharp, or abrasive materials?
- Does your process demand maximum durability and minimal downtime?
- Do you require custom belt profiles (cleated, sidewall, etc.)?
- Is your conveyor exposed to oil, heat, or harsh chemicals?
- Would reinforced belts (steel cord, fabric ply) improve performance?
If these requirements match your needs, a rubber conveyor belt is likely the optimal choice. Get in touch with a rubber conveyor belt manufacturer for tailored product recommendations.
Buyer’s Guide: How to Select the Best Conveyor Belt Material and Supplier
Finding the right conveyor belt material supplier is as important as selecting the correct belt type. Your supplier should offer not only a broad range of products, but also the technical expertise to match your requirements with the best solution for your industry, application, and budget.
Steps for Selecting a Conveyor Belt Material Supplier:
- Evaluate Your Application: Identify operational needs such as temperature range, load weight, chemical exposure, hygiene requirements, and desired belt lifespan.
- Shortlist Experienced Manufacturers: Use our directory to compare at least six conveyor belt material suppliers or manufacturers. Review each profile to examine their specializations, certifications (such as FDA, USDA, or ISO compliance), and technical support capabilities.
- Request Technical Data and Samples: Ask for product datasheets, material specifications, and—where possible—physical samples to test fit and compatibility in your system.
- Assess Customization and Support: Determine if the supplier can provide custom belt profiles, surface finishes, or reinforcements tailored to your process.
- Use Our RFQ Tool: Streamline your procurement process by sending a single request for quote (RFQ) to multiple suppliers simultaneously. Compare pricing, lead times, and after-sales services.
- Check References and Reviews: Look for testimonials or case studies from similar industries to verify supplier reliability and product performance.
Each conveyor belt material manufacturer has a dedicated business profile page that highlights their core competencies, certifications, and areas of expertise. Utilize our patented website previewer to get a quick overview of each company's specialties, and use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple conveyor belt material companies with a single message.
What Questions Should You Ask Conveyor Belt Suppliers?
- What are the recommended belt materials for my industry and process?
- Can you provide custom belt designs or reinforcements?
- What is the expected lifespan and maintenance schedule for your belts?
- Are your products compliant with relevant industry standards (FDA, USDA, ISO, etc.)?
- What is your typical lead time and after-sales support policy?
- Can you provide case studies or references from similar installations?
Frequently Asked Questions About Conveyor Belt Materials
What are the most common conveyor belt materials used in manufacturing?
The most common conveyor belt materials include rubber, thermoplastic polymers (polyurethane, PVC), metal (stainless steel, carbon steel), and fabric (nylon, polyester, cotton).
How do I choose the best conveyor belt material for my application?
Consider factors such as the type of material being conveyed, load weight, operating environment, sanitation requirements, temperature extremes, and budget constraints. Consult with experienced suppliers to match the belt material to your unique operational needs.
What is the difference between food-grade and industrial conveyor belts?
Food-grade conveyor belts are made from materials approved for direct food contact (such as FDA-compliant polyurethane or modular plastic) and are designed for easy cleaning and resistance to microbial growth. Industrial conveyor belts may prioritize abrasion resistance, chemical compatibility, or heat tolerance over hygiene.
How can I extend the lifespan of my conveyor belts?
Routine maintenance, proper tensioning, regular inspections, timely replacement of worn components, and selecting the appropriate belt material for your application are key to maximizing belt longevity.
Can conveyor belts be customized?
Yes, many manufacturers offer custom conveyor belts with specialized profiles, cleats, sidewalls, coatings, or reinforcements to suit specific operational challenges.
Industry Use Cases: Matching Conveyor Belt Materials to Your Sector
- Mining & Aggregate: Heavy-duty rubber and steel-reinforced belts for impact and abrasion resistance.
- Food Processing: Thermoplastic or modular plastic belts for hygiene, easy cleaning, and food safety compliance.
- Pharmaceuticals: Non-porous, chemical-resistant belts for contamination control.
- Automotive & Manufacturing: Metal and reinforced rubber belts for high-strength, high-temperature applications.
- Logistics & Distribution: Fabric or modular plastic belts for parcel handling and flexible routing.
- Recycling & Waste Management: Heavy-duty, oil-resistant rubber belts for durability and chemical resistance.
Discover the Right Conveyor Belt Material for Your Needs
Whether you're upgrading an existing conveyor system or designing a new installation, selecting the ideal conveyor belt material is a vital decision that impacts operational efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. From rubber and thermoplastic to metal and fabric belts, each material brings unique advantages tailored to specific industries and applications.
Ready to take the next step? Use our comparison tools to evaluate the top conveyor belt material suppliers, request technical guidance, and obtain competitive quotes. Not sure which material is right for your application? Contact our conveyor belt experts today for personalized assistance and product recommendations.








 Conveyor Belting
Conveyor Belting Conveyor Systems
Conveyor Systems Conveyors
Conveyors Hosereels
Hosereels Industrial Lubricants
Industrial Lubricants Lubricators
Lubricators Screw Conveyors
Screw Conveyors Pneumatic Conveyors
Pneumatic Conveyors AGV
AGV Air Pollution Control
Air Pollution Control Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Blowers
Blowers Cranes
Cranes Deburring Machinery
Deburring Machinery Dust Collectors
Dust Collectors Heaters
Heaters Hose Reels
Hose Reels Mezzanines
Mezzanines Modular Buildings
Modular Buildings Storage Racks
Storage Racks Ultrasonic Cleaners
Ultrasonic Cleaners Work Benches
Work Benches