A drive belt is attached to a few engine bay accessories. Depending on the type of car, the accessories may vary, but the AC compressor, alternator, fan clutch, and water pump are the most frequent ones. Read More…
Our conveyor belts are ISO 9002 and FDA certified. We can use our belts in nearly every industry, from transmission timing belts to conveyor belts for foods.
Creating conveyor belts at Fabrication Unlimited such as rubber belting, flat belts, endless belting, PVC, urethane belting, timing belts, cleated belting, specialty unscrambler belts (made-to-order), & corrugators belts, can be done with fast turn around for all fabricated belting offered. Serving food processing, agricultural, pharmaceutical, recycling, beverage and other industries.

Custom conveyor belting is fabricated by Beltservice Corporation and available through our distributors or OEMs. From this conveyor belt manufacturer, you will find agricultural, cleated, elevator, food handling, heat-resistant, heavy-duty and light-duty, incline, package-handling belting and more.

Come to Con-Belt Inc. for quality flat belts. Established in 1991, we have over twenty years of manufacturing experience and can meet your specifications and exceed your expectations. All of our products are made with pride in U.S. and are compatible and interchangeable with most major manufacturers’ conveyor equipment. Contact us today for further information about the products we offer.

More Drive Belt Manufacturers
These moving parts receive power from the belt, which enables them to keep the car moving. Therefore, preserving the vehicle's cooling system and engine output is crucial. The belt allows travel through three additional pulleys that are made to fit the belt snugly and prevent sliding. Belts are forced into the shape of idler pulleys by being pressed up against them.
The lifespan of a drive belt is at least 10,000 miles. In front-wheel drive automobiles, cranks or breaks can be seen from the side. Likewise, it can be seen from the front of cars with boxer engines or rear-wheel drive. In some older vintage rear-wheel drive vehicles, the drive belt also powers the front engine fan. Some engine designs employ two depending on the setup and the device layout. The smooth backside of the belt drives various components in some engine configurations. The design usually only applies to parts requiring minimal torque or having a large enclosed angle.
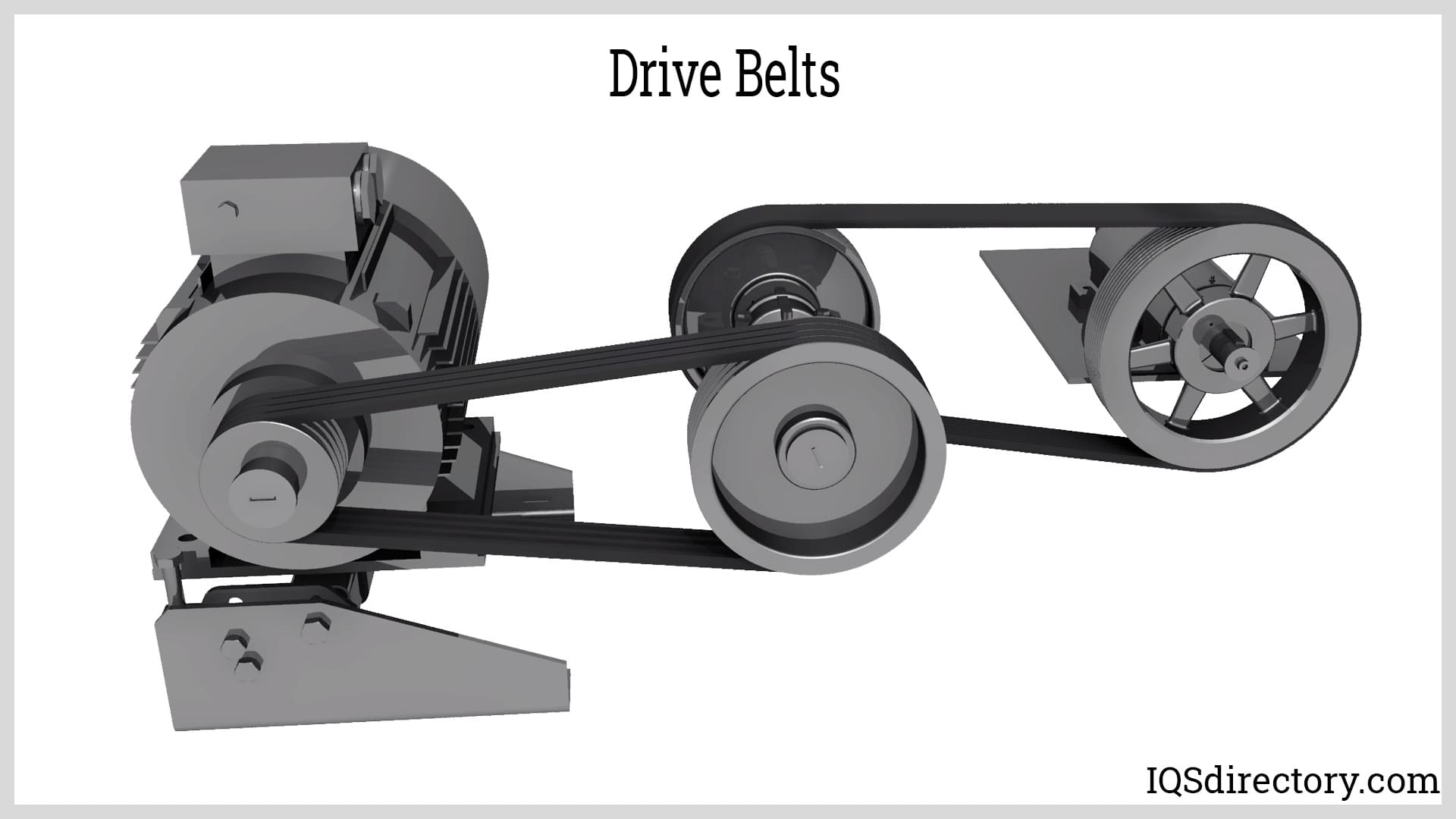
Working Principle Of Drive Belts
A drive might have simple or complex operations depending on the engine architecture. To maintain the devices' connection to the drive belt, the belt, idler, tensioner, and pulleys cooperate. With the components mentioned above, the belt drive and the engine may only run if it's functioning. Once the engine is running until the car is turned off, the serpentine belt keeps working. The power used to control the crankshaft as the primary energy source is obtained from the combustion process.
Types Of Drive Belts
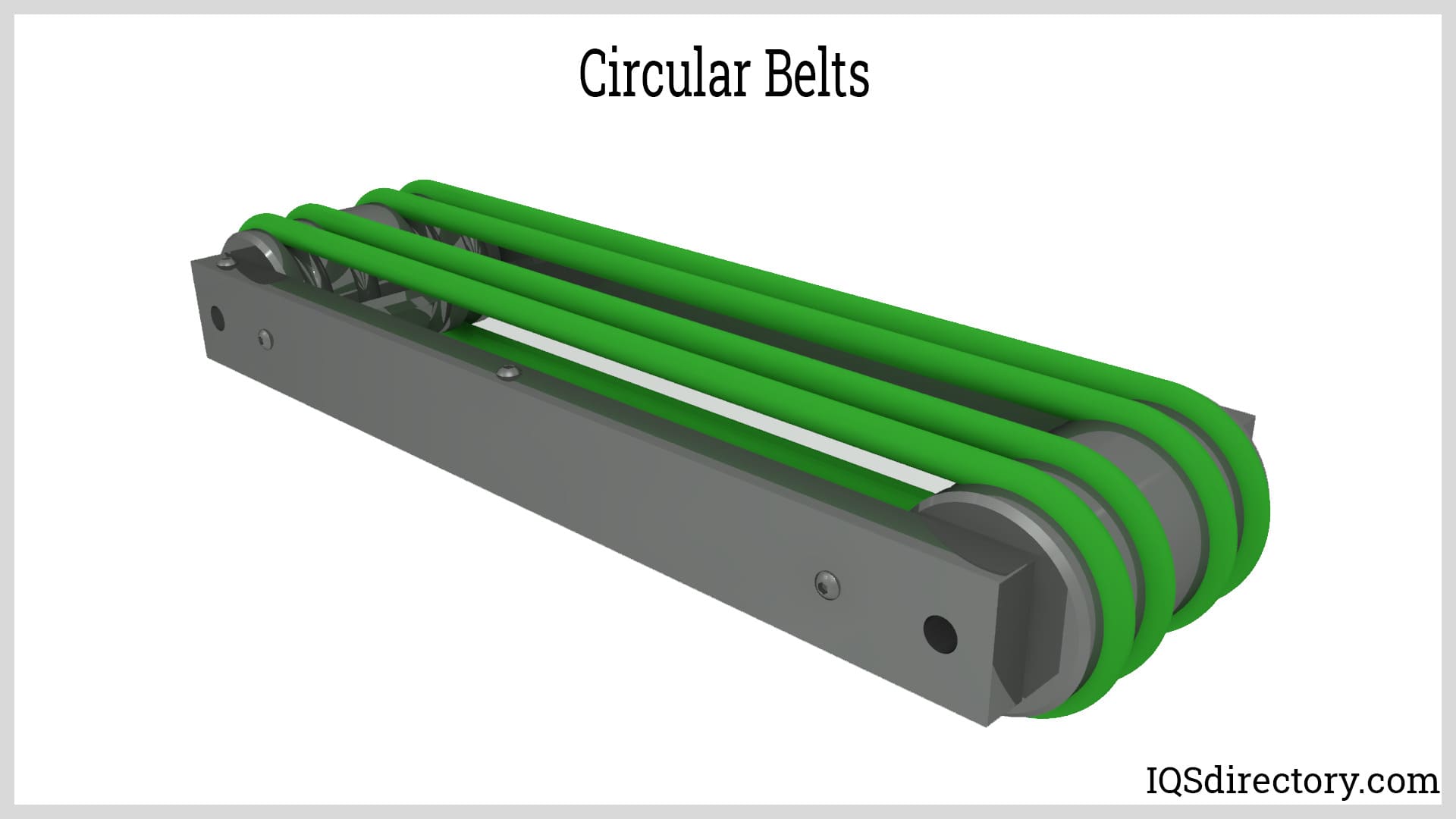
Circular Belts
This belt forms a circle with its cross-section. Circular belts are used when the shaft distance is greater than five meters. They are employed for the transmission of high power. Circular belts are also used when less initial strain is needed, and there is no need for vibration or noise.
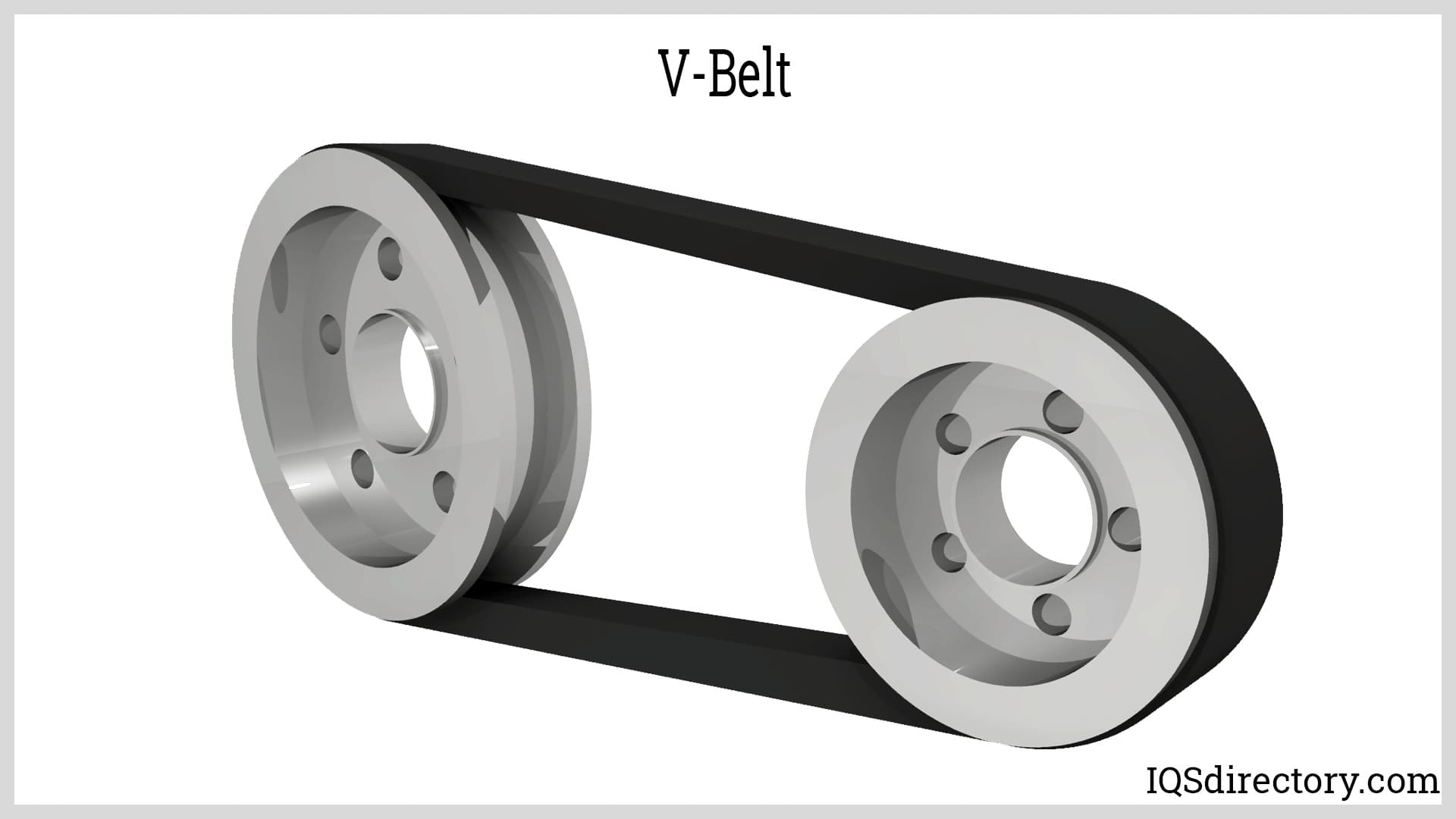
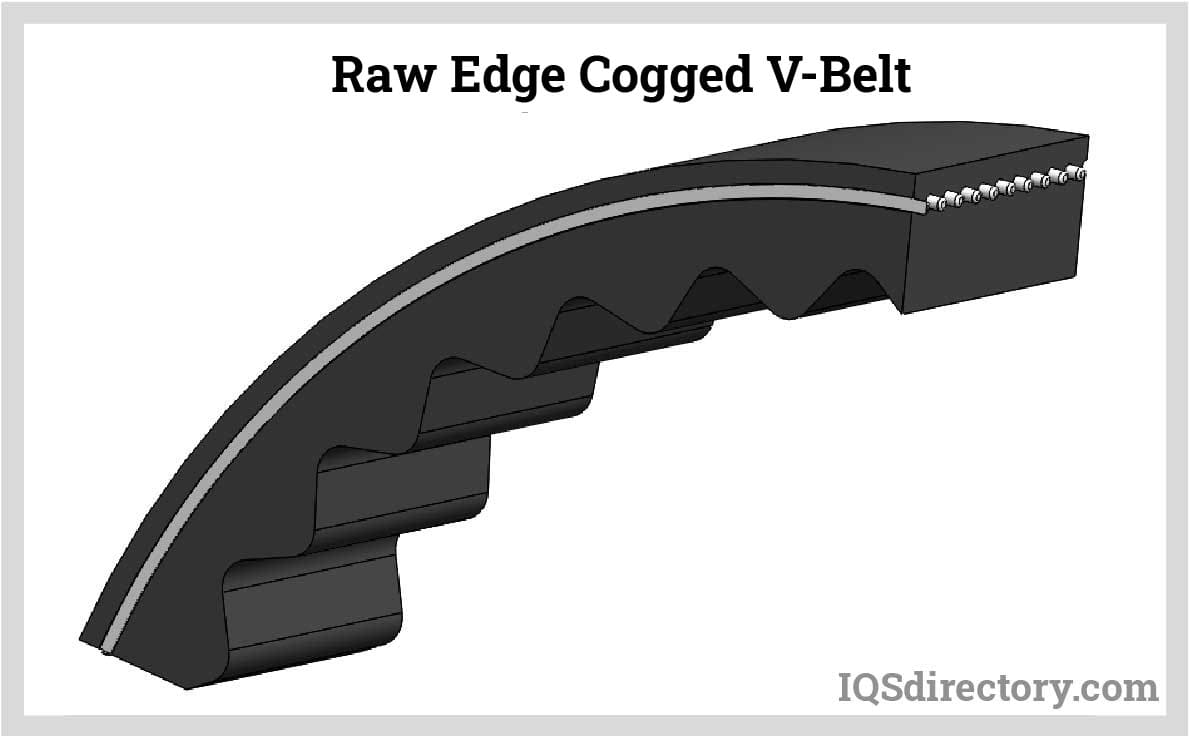
V-Belt
V-belts are utilized for moderate speed and high power when the shaft distance is less than two meters. A trapezoidal cross-section has V-belts. Multiple drives are conceivable with a belt.
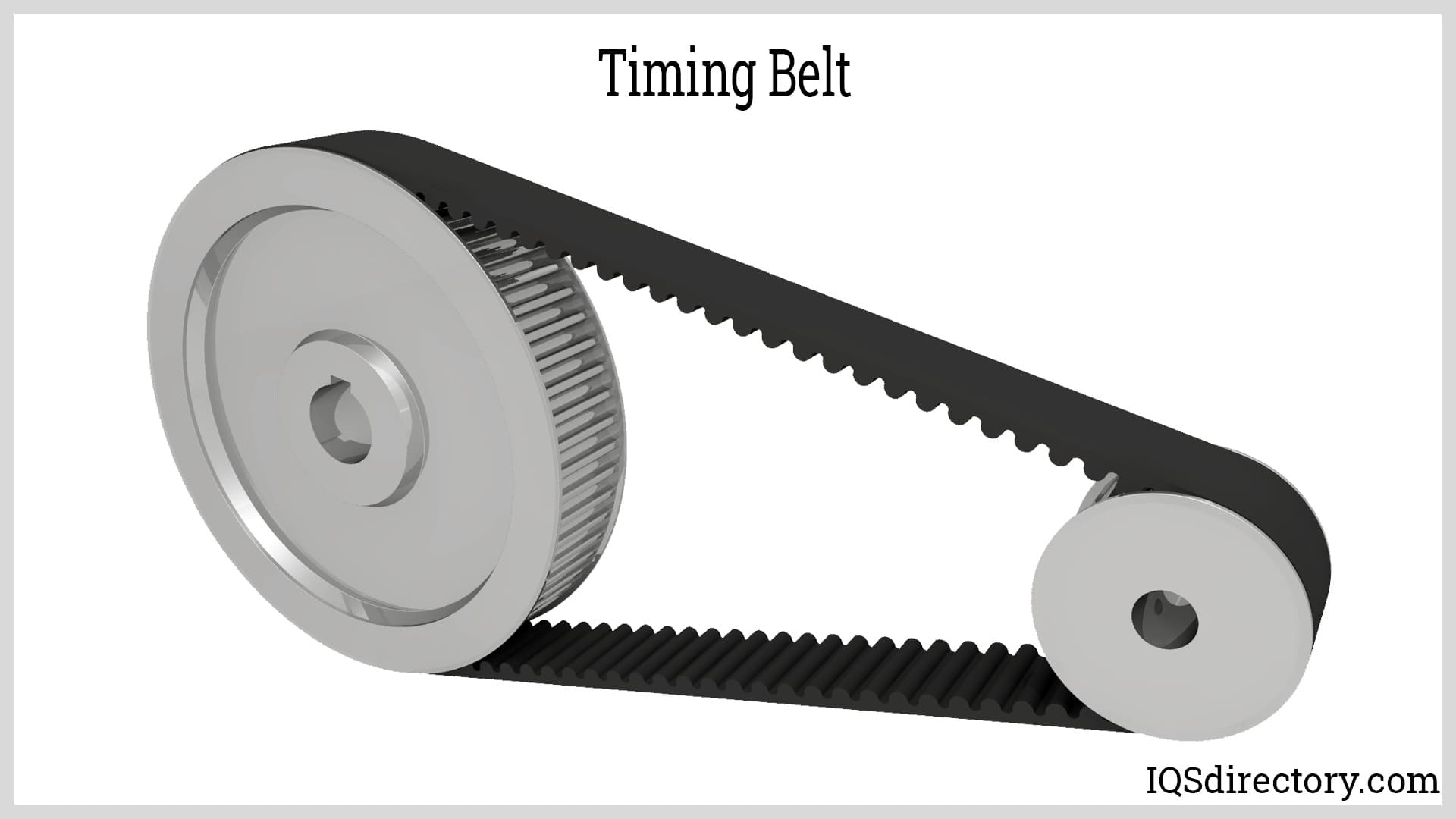
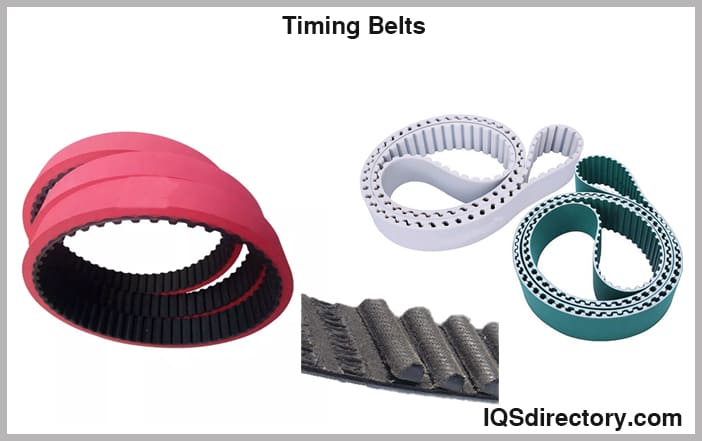
Timing Belt
This belt is an alternative style. Timing belts are primarily used to transmit power inside the system (internal combustion type) because they have a positive drive.
Types of Belt-Drive
There are five types of belt drives:
- Jockey pulley drive
- Open belt drive
- Fast and loose cone pulley
- Closed or crossed belt drive
- Stepped cone pulley
Applications of Drive Belts
There are several applications for belt drives, including:
- Moving objects with power
- The mill industry
- Conveyors
Functions Of a Drive Belt
The purposes of a drive belt in an automobile engine are listed below:
- A drive belt's main function is to drive or power an engine's accessories.
- Drive belts use one source of energy to power multiple components.
- They increase the mechanical efficiency of the engine.
- Since a drive belt powers the engine water pump, it will stop running and cause overheating if it breaks.
- Also, hydraulic power steering is driven by a belt.
- An electric power alternator will stop working if the device is disabled.
Advantages Of Using Drive Belts
Below are the benefits of a drive belt used in an automotive engine:
- Serpentine belts consume less space and are more effective than the older multiple-drive belt system.
- The belt can undergo an increase in tension without stretching.
- Since higher tension reduces slip, belt life and mechanical efficiency are increased.
- The belt is much easier to maintain and replace since there is no need for multiple belts to be removed.
- Since only one tensioner belt is needed for all the peripheral components, they can be mounted on the engine without swiveling.
- Less slip allows a serpentine belt to work well on lower-ratio pulleys as the engine load is reduced.
- Fuel economy and available power are increased.
- The tendency of flip over in the pulley groove is eliminated.
Disadvantages Of Drive Belts
- Slip and creep-related power loss
- Cannot be employed over small distances
- Increased chances of breaking
- Wear results if the temperature is over 185 °F (85 °C)
- Because of slipping, the angular velocity ratio is sometimes constant or equal to the ratio of the pulley's diameter
- Vehicle loses multiple critical functions if the belt breaks
- Vehicle becomes unusable when engine cooling is terminated
- Lack of redundancy
- Breakage of the single belt means loss of all accessories
Choosing the Right Drive Belts Manufacturer
To make sure you have the most beneficial outcome when purchasing Drive Belts from a Drive Belts Company, it is important to compare at least 4 Manufacturers using our list of Drive Belts suppliers. Each Drive Belts Supplier has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each Drive Belts business website using our proprietary website previewer to get an idea of what each business specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple Drive Belts businesses with the same form.










 Conveyor Belting
Conveyor Belting Conveyor Systems
Conveyor Systems Conveyors
Conveyors Hosereels
Hosereels Industrial Lubricants
Industrial Lubricants Lubricators
Lubricators Screw Conveyors
Screw Conveyors Pneumatic Conveyors
Pneumatic Conveyors AGV
AGV Air Pollution Control
Air Pollution Control Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Blowers
Blowers Cranes
Cranes Deburring Machinery
Deburring Machinery Dust Collectors
Dust Collectors Heaters
Heaters Hose Reels
Hose Reels Mezzanines
Mezzanines Modular Buildings
Modular Buildings Storage Racks
Storage Racks Ultrasonic Cleaners
Ultrasonic Cleaners Work Benches
Work Benches