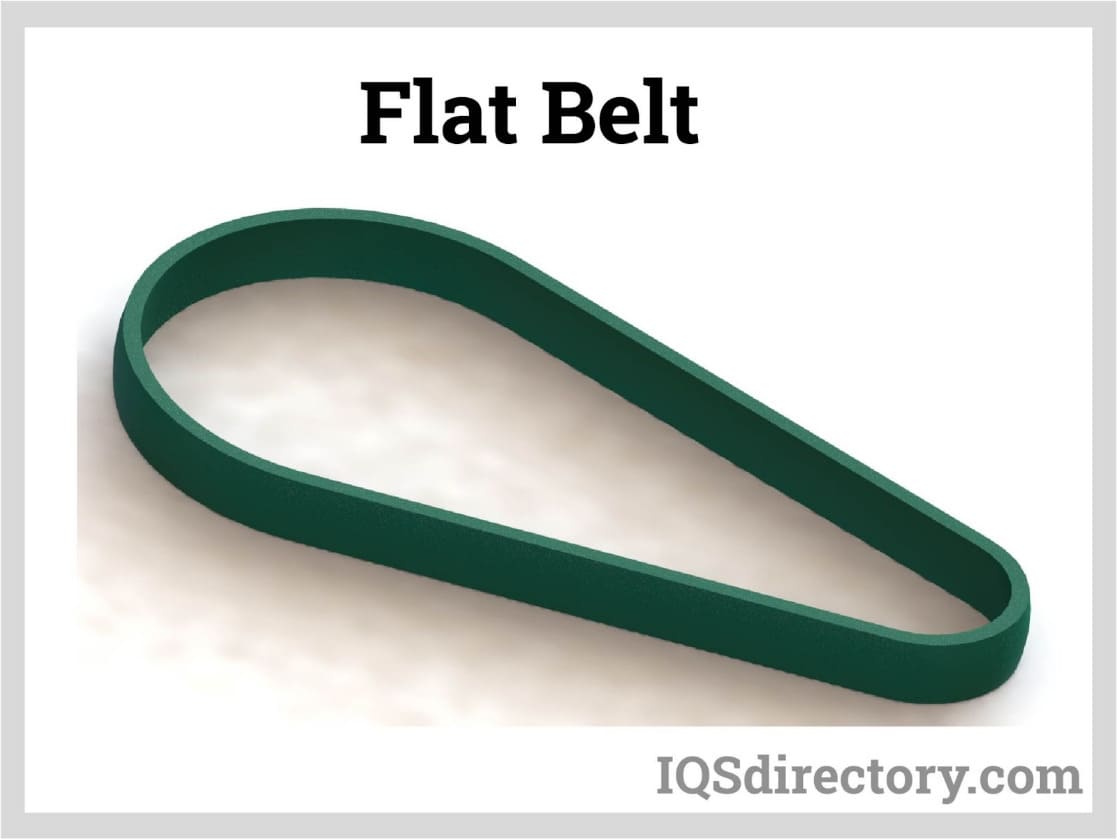
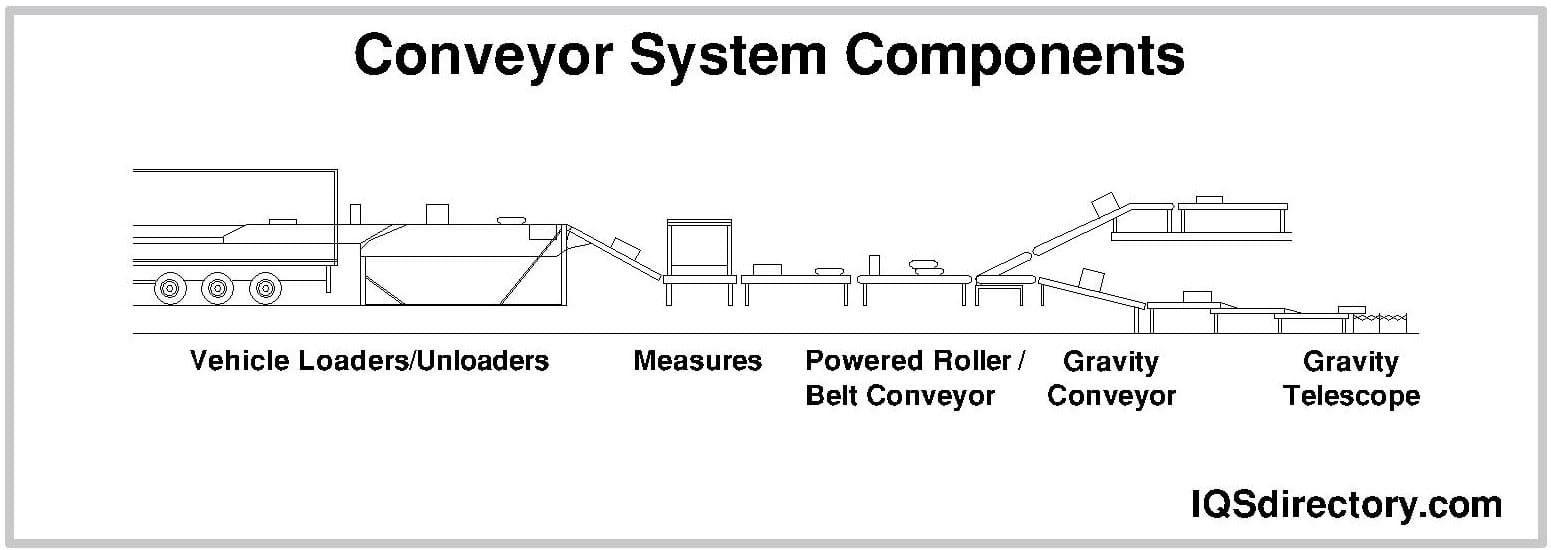
Flat belts may be used as part of conveyance systems to move things directly by directly setting items upon them. A continuous flat belt may be made of either natural or synthetic cloth (ex., polyester, nylon) and is paired with several motorized pulleys to form a conveyor. Read More…
Our conveyor belts are ISO 9002 and FDA certified. We can use our belts in nearly every industry, from transmission timing belts to conveyor belts for foods.
Creating conveyor belts at Fabrication Unlimited such as rubber belting, flat belts, endless belting, PVC, urethane belting, timing belts, cleated belting, specialty unscrambler belts (made-to-order), & corrugators belts, can be done with fast turn around for all fabricated belting offered. Serving food processing, agricultural, pharmaceutical, recycling, beverage and other industries.

Custom conveyor belting is fabricated by Beltservice Corporation and available through our distributors or OEMs. From this conveyor belt manufacturer, you will find agricultural, cleated, elevator, food handling, heat-resistant, heavy-duty and light-duty, incline, package-handling belting and more.

Come to Con-Belt Inc. for quality flat belts. Established in 1991, we have over twenty years of manufacturing experience and can meet your specifications and exceed your expectations. All of our products are made with pride in U.S. and are compatible and interchangeable with most major manufacturers’ conveyor equipment. Contact us today for further information about the products we offer.

More Flat Belt Manufacturers
More commonly, flat belts are paired with many motorized pulleys to operate machinery. In addition, center drives and nose bars are optional components that can include depending on the needs of a particular application.
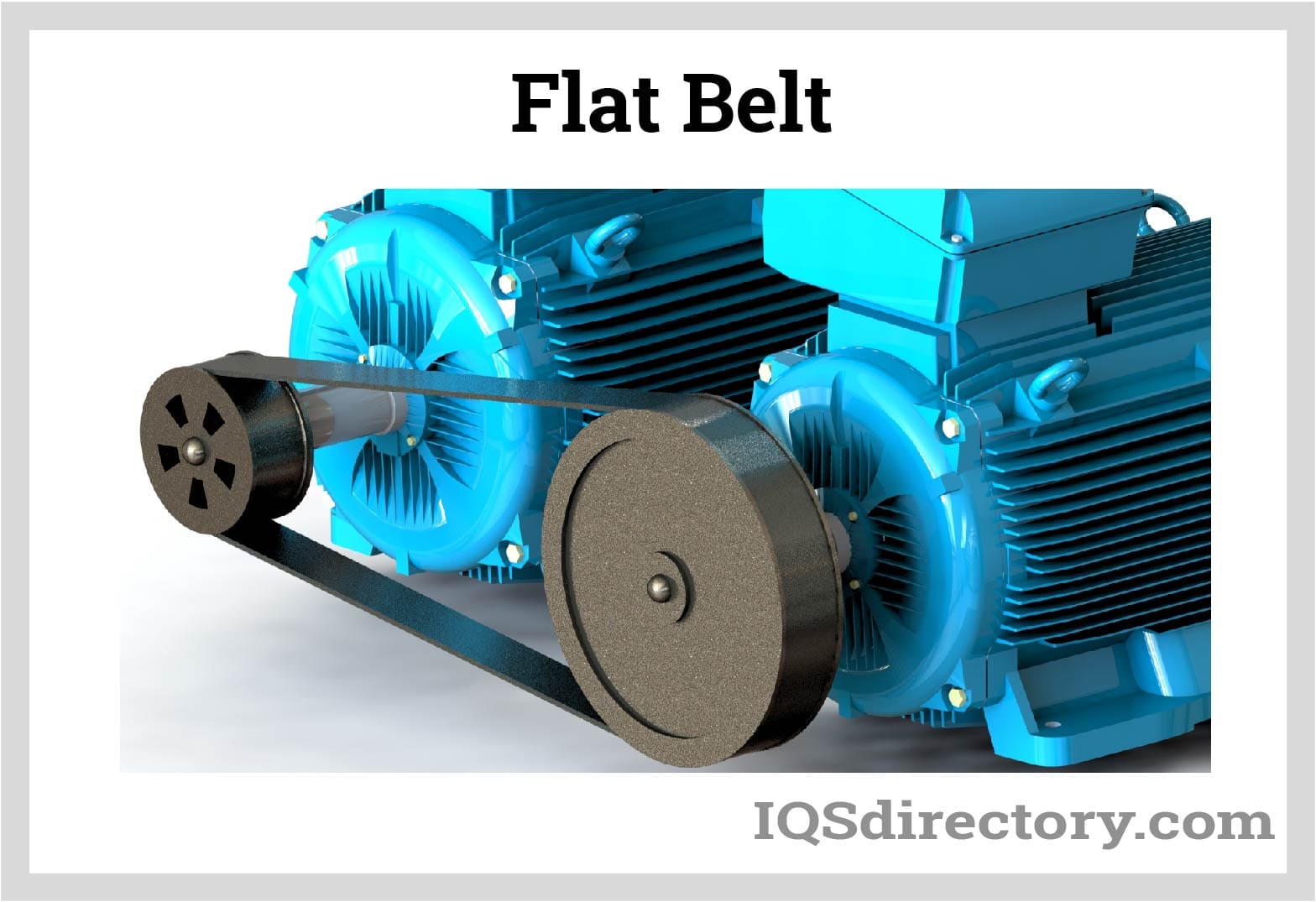
Material of Flat Belts
This belt is adaptable because it can be built from various materials. The substance chosen is determined by its substance, as well as by its shape and size. For instance, it is unlikely that a narrow, flat belt composed of natural rubber will be employed as a conveyor during a heat-treating procedure.
Rubber's narrowness makes it difficult to transport goods from one place to another. Second, natural rubber has a poor tendency to withstand high temperatures, making it unsuitable for environments where it may be exposed to high temperatures for an extended period. Wide, heat-resistant synthetic rubber or plastic belts would be a more practical choice for this situation.
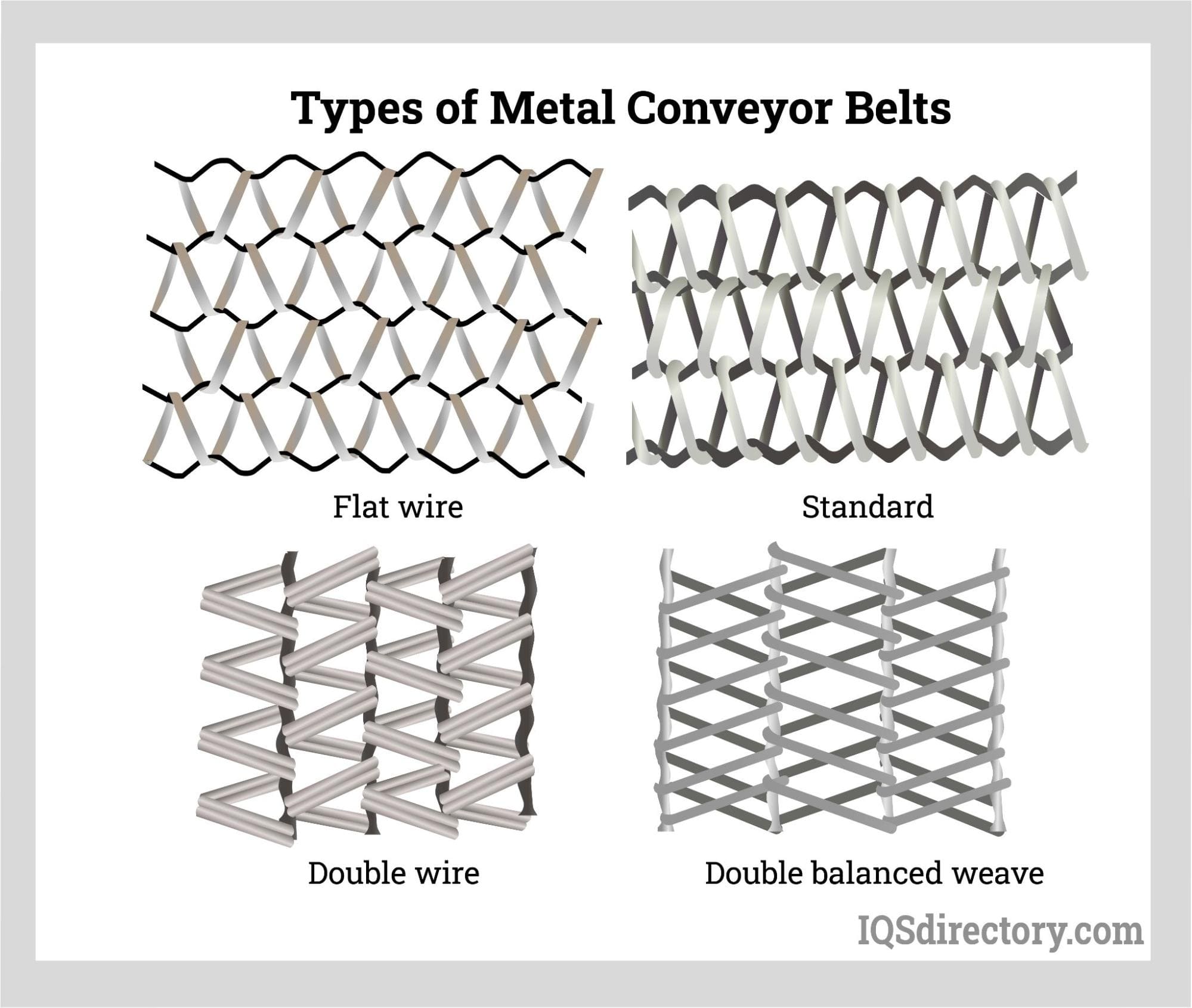
Likewise, other situations can more appropriately use belts made of metal for other situations. Other materials, including neoprene, silicone, polyurethane (often mistakenly referred to as urethane), and various synthetic rubber, nylon, PVC, and Teflon™ are potential materials for flat belt fabrication, and each is better suited for specific applications.
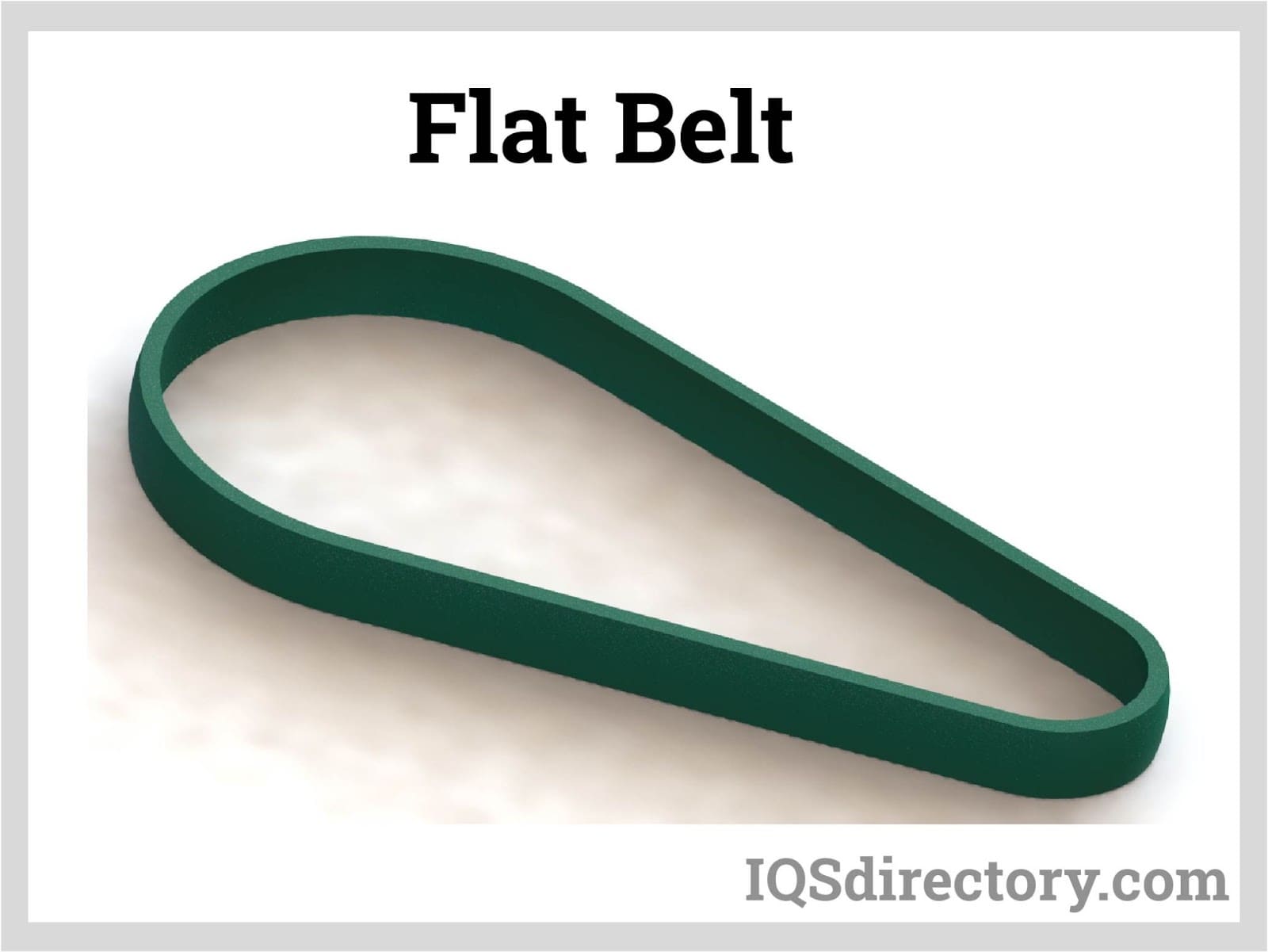
Common Problems Encountered With Flat Belts
- The conveyor runs to one side at a specific location on the structure.
Reason: Material buildup on idlers (pulleys used to guide the belt)
Solution: Get rid of accumulation, maintain the conveyor better, and put in scrapers or other cleaning equipment.
Reason: Stuck idlers
Solution: Idlers should be freed, and staff should improve maintenance and lubrication.
Reason: Idlers or pulleys that are not aligned with the belt's middle line.
Solution:Adjust idlers in the affected area as a solution.
Reason: A misaligned conveyor frame or other construction
Solution: Straighten the damaged area as a solution.
Reason: The idler's feet are not centered on the belt.
Solution: Adjust idlers in the affected area as a solution.
Reason: A level structure
Solution: Improve the area's structure.
- On the conveyor, a specific belt segment always runs to one side.
Reason: Belt not squarely spliced or connected
Solution: Re-splice and remove the damaged splice.
Reason: The belt is bowed.
Solution: For a brand-new belt, this issue should go away during break-in; in rare cases, the belt needs to be straightened or replaced; check how the belt rolls are stored and handled.
- The conveyor's full length or a significant portion of the belt runs to the side.
Reason: Belt swerving across the loading region and around the tail pulley
Solution: Install training idlers on the return side before the tail pulley as a solution.
Reason: Poor loading or off-centering
Solution: Adjust the chute so that the load is on the center of the belt, and discharge the material in the direction of the belt's motion at, or close to, belt speed.
Reason: Material buildup on idlers
Solution: Get rid of accumulation, maintain them better, and put in scrapers or other cleaning equipment.
Reason: Idlers or pulleys that are not aligned with the belt's middle line
Solution: Adjust idlers in the affected area as a solution.
Reason: A misaligned conveyor frame or other construction
Solution: Straighten the damaged area as a solution.
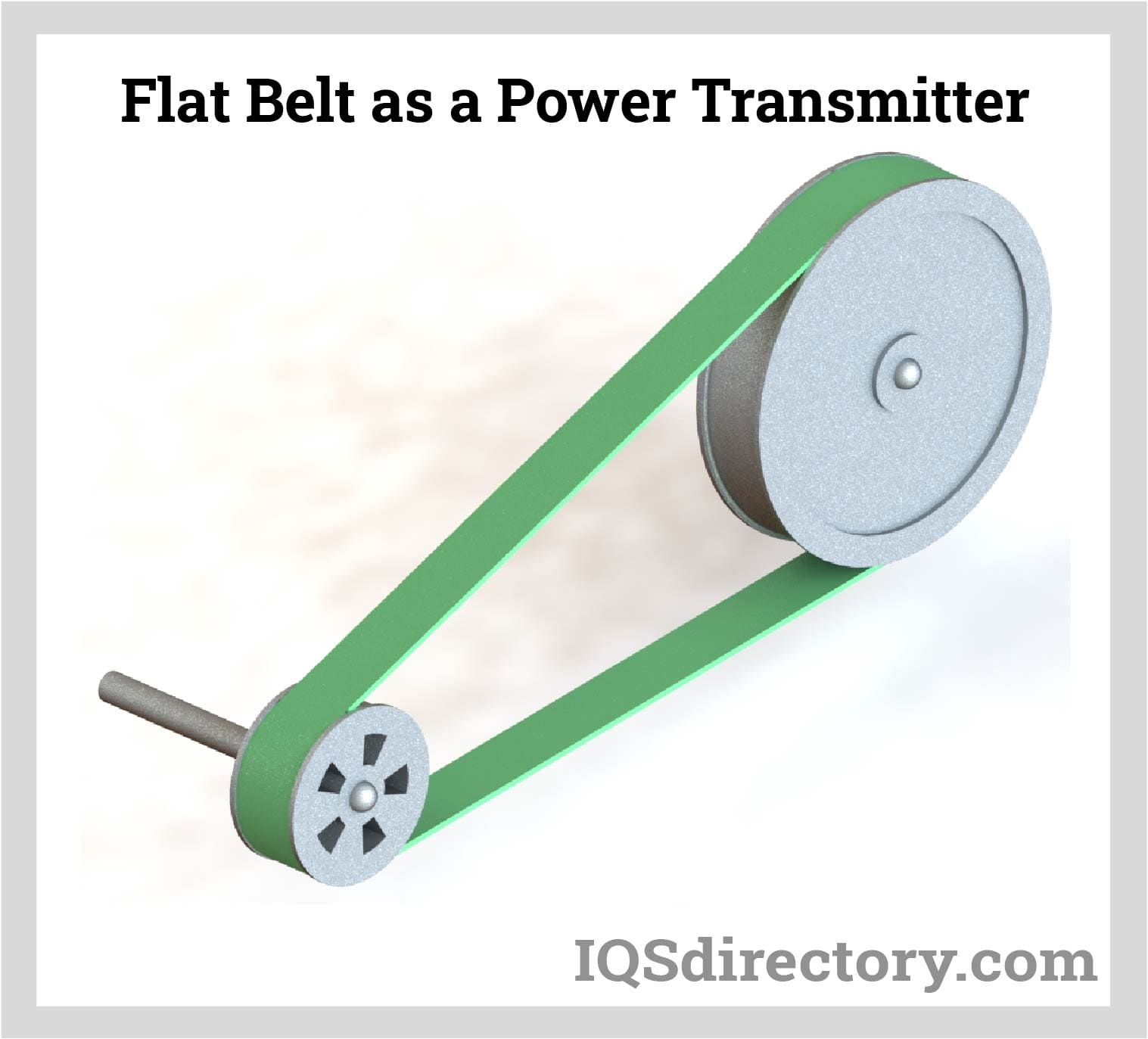
Applications of Flat Belts
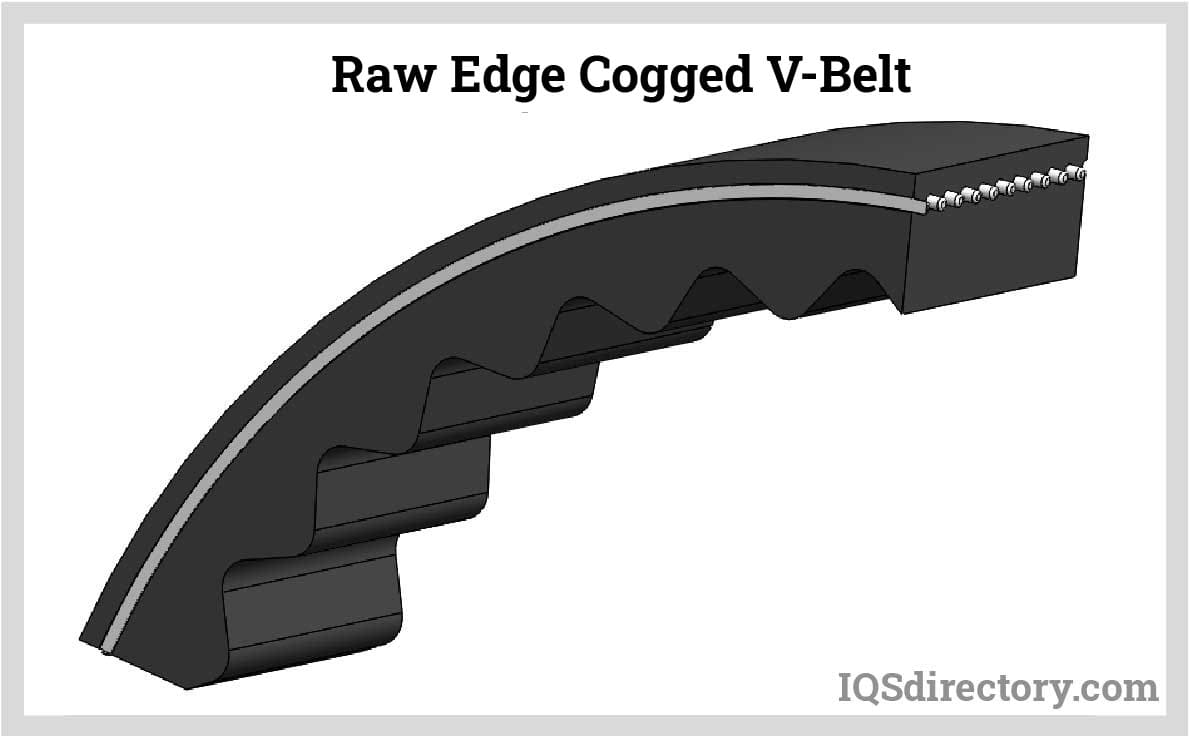
Cleats, lamination, perforations, profiles, or side walls could all be included in a flat belt. Many different industries employ flat belts. For many years, flat belts have been used in manufacturing.
They have been, and still are, widely used in agricultural equipment, including threshing machines, silo blowers, balers, pumps, and generators. They are also extensively utilized in many of the equipment used in logging and mining applications.
Additionally, industrial coating, cooling, draining, drying, and heating applications can use flat belts. Typically, the application of a flat belt is determined by its width and material.
Wider flat belts are typically utilized in conveying systems, while narrower flat belts are typically employed as parts of machines. Like most belt types, flat belts can have seams or be infinite.
Choosing the Proper Flat Belts Manufacturer
To make sure you have the most productive outcome when purchasing Flat Belts from a Flat Belts Manufacturer, it is important to compare at least 6 Suppliers using our list of Flat Belts companies. Each Flat Belts Supplier has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each Flat Belts company website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each company specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple Flat Belts companies with the same quote.










 Conveyor Belting
Conveyor Belting Conveyor Systems
Conveyor Systems Conveyors
Conveyors Hosereels
Hosereels Industrial Lubricants
Industrial Lubricants Lubricators
Lubricators Screw Conveyors
Screw Conveyors Pneumatic Conveyors
Pneumatic Conveyors AGV
AGV Air Pollution Control
Air Pollution Control Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Blowers
Blowers Cranes
Cranes Deburring Machinery
Deburring Machinery Dust Collectors
Dust Collectors Heaters
Heaters Hose Reels
Hose Reels Mezzanines
Mezzanines Modular Buildings
Modular Buildings Storage Racks
Storage Racks Ultrasonic Cleaners
Ultrasonic Cleaners Work Benches
Work Benches