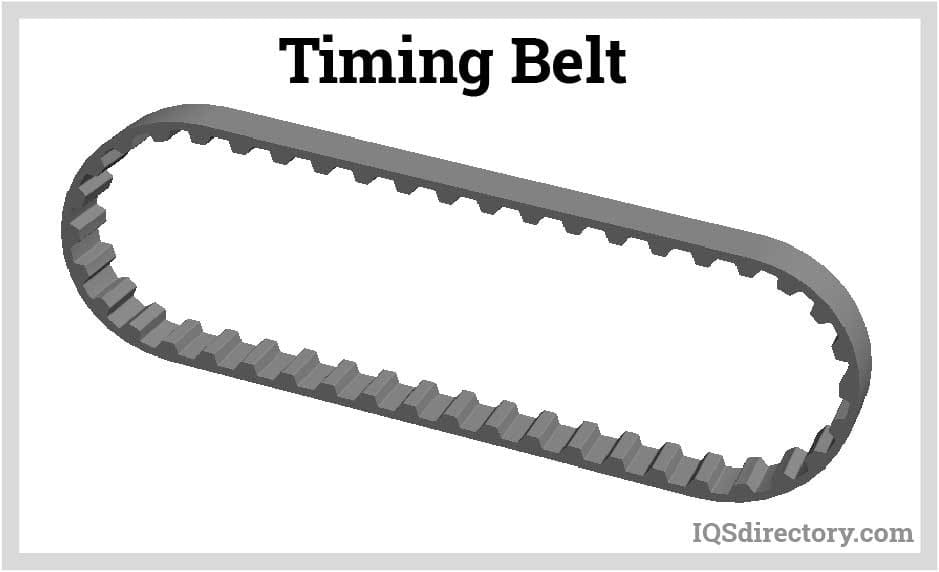
An internal combustion engine uses a timing belt to coordinate the motion of the crankshaft and camshaft. It is made with a precise hard tooth that interlocks with the two camshafts, the crankshaft’s cogwheel, and both. Read More…
Our conveyor belts are ISO 9002 and FDA certified. We can use our belts in nearly every industry, from transmission timing belts to conveyor belts for foods.
Creating conveyor belts at Fabrication Unlimited such as rubber belting, flat belts, endless belting, PVC, urethane belting, timing belts, cleated belting, specialty unscrambler belts (made-to-order), & corrugators belts, can be done with fast turn around for all fabricated belting offered. Serving food processing, agricultural, pharmaceutical, recycling, beverage and other industries.

Custom conveyor belting is fabricated by Beltservice Corporation and available through our distributors or OEMs. From this conveyor belt manufacturer, you will find agricultural, cleated, elevator, food handling, heat-resistant, heavy-duty and light-duty, incline, package-handling belting and more.

Come to Con-Belt Inc. for quality flat belts. Established in 1991, we have over twenty years of manufacturing experience and can meet your specifications and exceed your expectations. All of our products are made with pride in U.S. and are compatible and interchangeable with most major manufacturers’ conveyor equipment. Contact us today for further information about the products we offer.

More Timing Belting Manufacturers
Timing belts are frequently seen in front of the engine and are frequently covered to keep out dust and other debris. But since 2008, a few engines have been using "wet timing belts," in which the belt is treated with engine oil to lessen friction. In addition, the timing belt may drive additional parts in some engine types, like the water pump and oil pump.
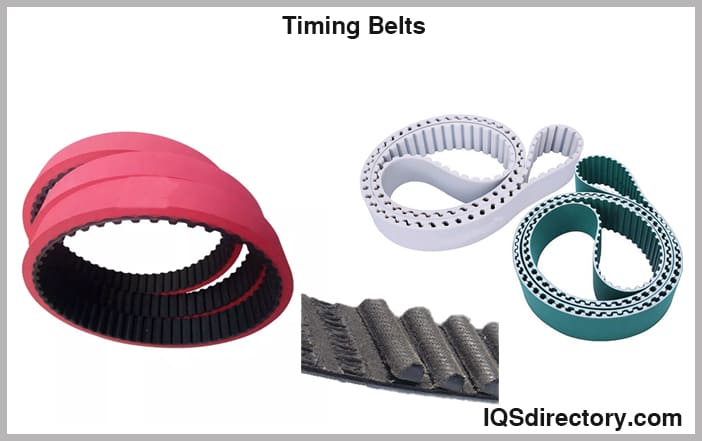
Timing belts are normally constructed of rubber. The belt's structure is strengthened by corded fibers that serve as tension members, and a fabric covering strengthens the toothed surface.
Higher temperatures and contact with motor oil cause rubber to deteriorate. As a result, a timing belt's lifespan is reduced in hot or leaky engines. Water and antifreeze can also shorten the reinforcing cords' life; thus, a belt should not come into contact with water that has a quick drainage system.
With their trapezoid-shaped teeth, older belts have high tooth wear rates. Curved teeth are now possible, allowing for quieter, longer-lasting products. Timing belts that don't meet manufacturer specifications may stretch at high rpm, delaying the cam and, consequently, the ignition. Stronger aftermarket belts won't stretch and maintain timing. A broader belt strengthens when creating the timing belt, while a narrower belt lightens it and lowers friction.
Timing belts fail due to delamination and unraveling of the fiber cores or stripped teeth (leaving a smooth belt stretch where the driving gear may slip). Due to the nature of the high-tensile fibers, belt breakage is rare. However, often ignored, dirt and debris combined with oil and grease can steadily deteriorate the belt's materials, speeding up the wear cycle and leading to early belt failure.
Functions of Timing Belts
The following are the purposes of timing belts in automobile engines:
- Due to the timing belt's dependence on the piston and valve control, the combustion process is made possible.
- To control the operation of the valves, it joins the crankshaft and camshaft.
- Thanks to the timing belt, the engine's valves are precisely timed to open and close.
- The timing belt controls the valve using the same mechanical energy from combustion.
- A timing belt or chain also serves the purpose of avoiding a crucial degree of piston-to-valve contact.
Timing Belt Working Principle
Timing belts operate in an accurate and timely manner. The combustion process in engines is feasible even if the crankshaft needs to be rotated. Once the camshafts are synchronized, the valve can open and close to allow fuel and air to reach the combustion chamber. This rotation also regulates the exhaust valve, allowing the exhaust to exit. This process is carried out in unison. Crankshafts are made to run at half the speed of the camshaft because they coordinate their movements. For instance, a camshaft turn is produced by two crankshaft spins. Timing belt tension is designed because the timing belt needs tension to function properly. Automatic timing belt tensioners are used in modern automobiles and don't need to be adjusted. However, the belt would occasionally get loose in older cars, necessitating correction. Timing is so crucial that if one movement is off, it can damage the engine's efficiency and cause misfires and a loss of power.
Timing Belt Tooth Profiles
Timing belt teeth can be configured in various ways, depending on the required use and climate. We discuss some of these timing belt profiles below.
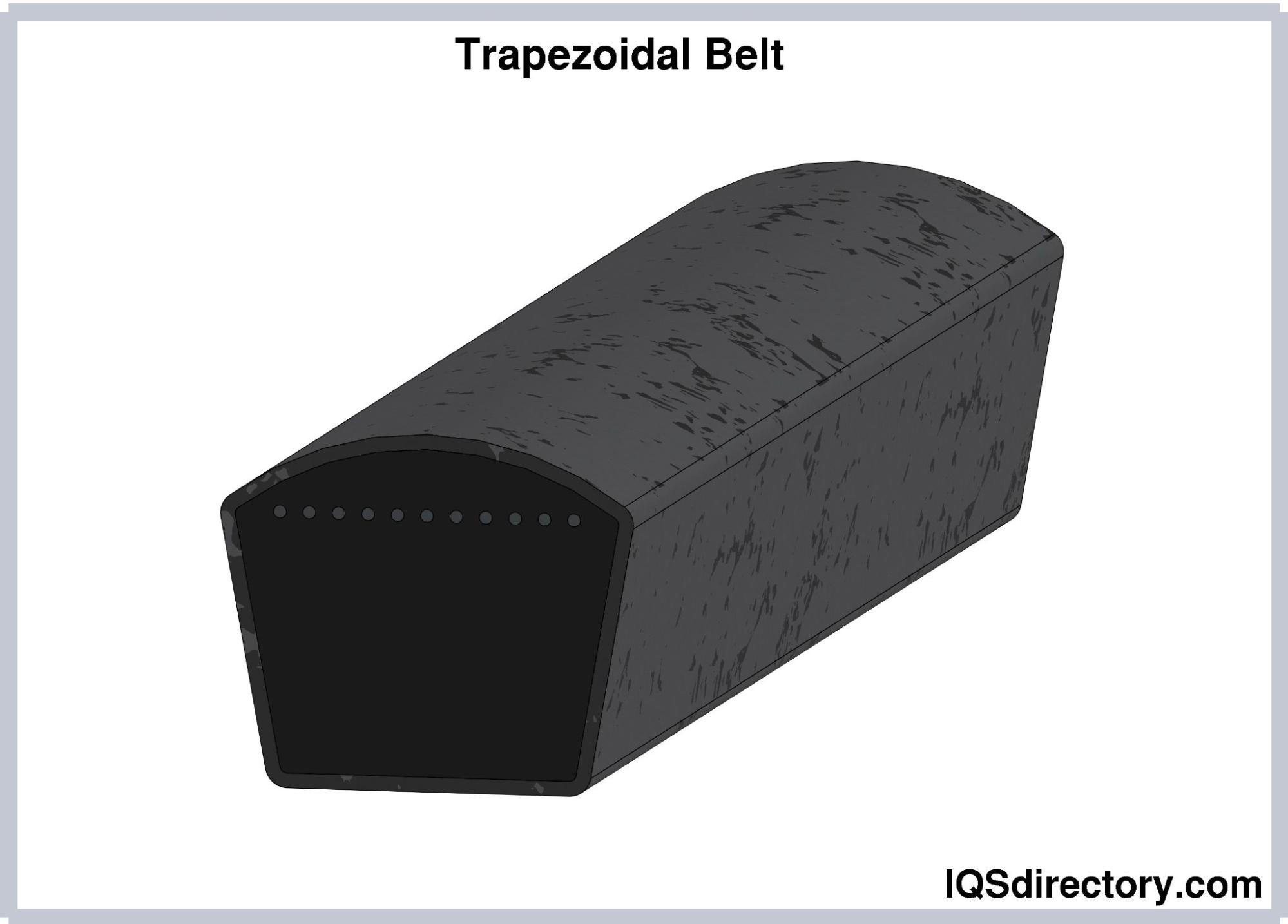
Trapezoidal Belts
Teeth with a trapezoidal shape are very good at transmitting forces. However, teeth with this harsher, more blunt design tend to wear out quickly at higher levels of torque or speed. Nevertheless, despite their flaws, trapezoidal teeth continue to be widely used and are frequently the first option for linear positioning and precision conveying belts.
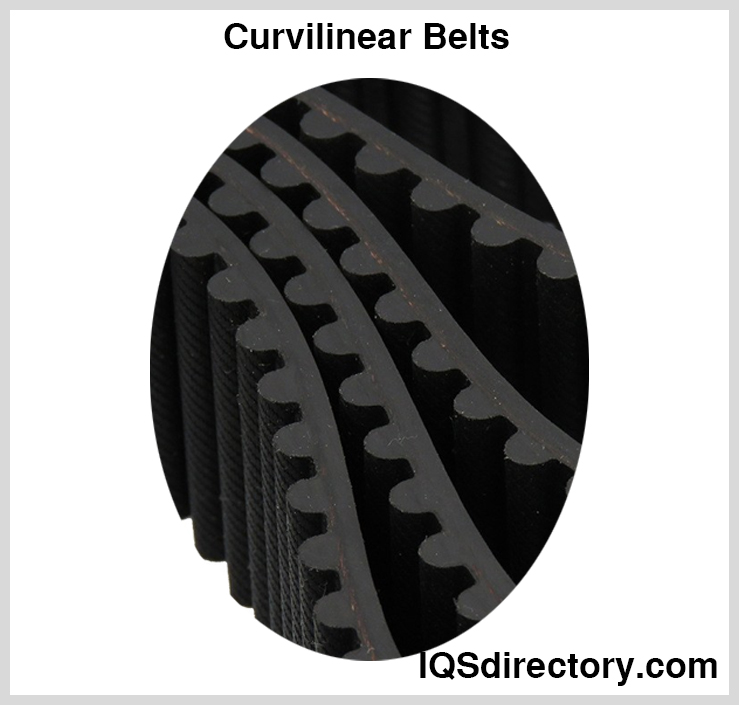
Curvilinear Belts
Curvilinear teeth lessen the chance of tension loss and the high concentration of force that trapezoidal teeth encounter by having a smoother and more rounded tooth form. However, although it may seem like a significant advance, curvilinear belts have certain disadvantages of their own.
Teeth with this profile will likely experience more play between the belt's teeth and the pulleys' grooves. Backlash is a problem that frequently leads to less precise belt alignment and diminished performance.

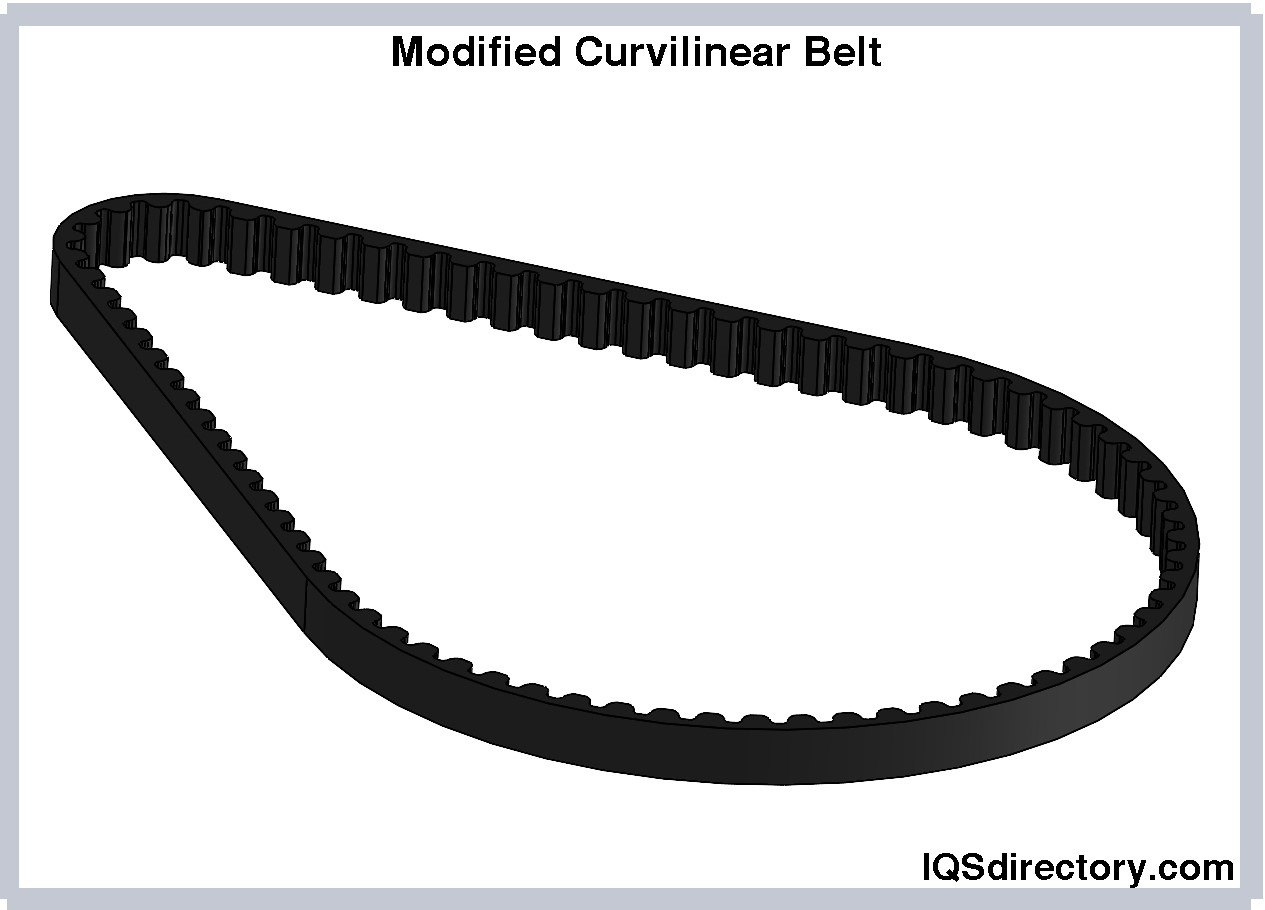
Modified Curvilinear Belts
The advantages of both trapezoidal and curvilinear tooth profiles are combined in modified curvilinear belts. These belts can efficiently transmit higher speed and torque forces without sacrificing durability because they have less tooth depth and steeper sides. So, customized curvilinear belts are frequently the first option for demanding industrial applications.
Timing Belt Applications
Here are a few applications for timing belts.
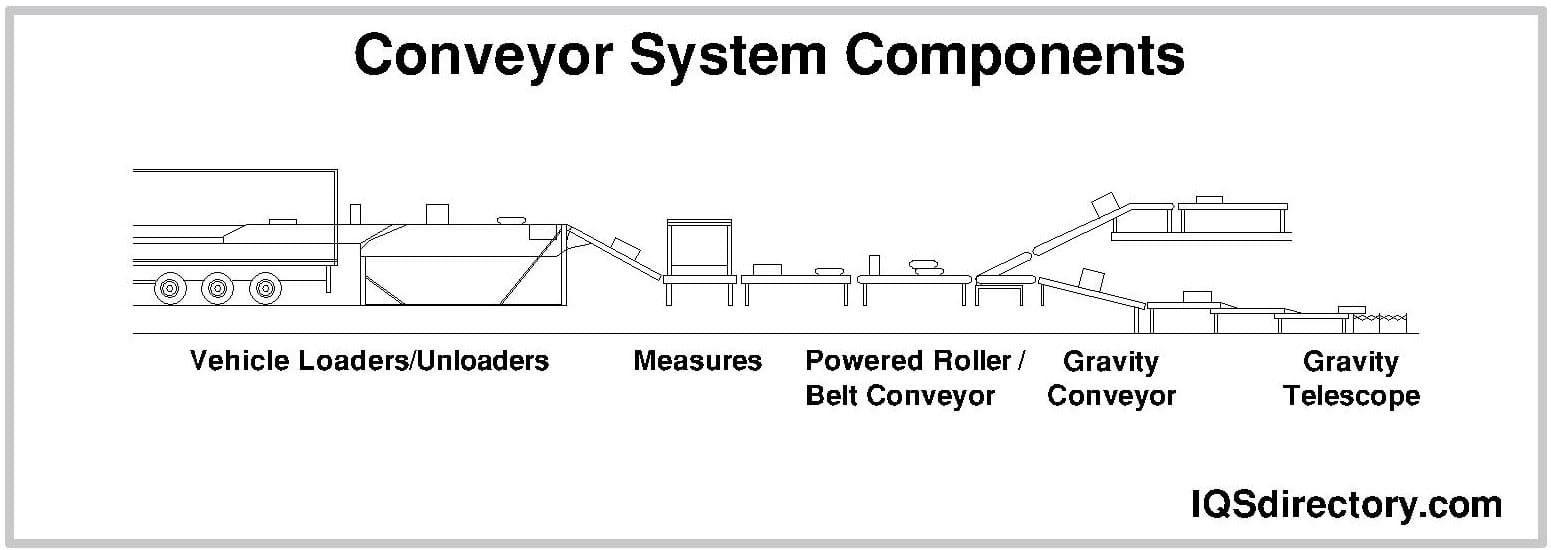
- Conveyor systems
- Printers
- Sewing machines
- Automobiles
- Home appliances
- Toys
Advantages of Timing Belts
Timing belts have some benefits over flat or round belt drives, such as:
- Rust- and abrasion-resistant
- Minimal vibrations
- No slippage
- Minimal noise
- Timing and motion with precision
- 98% mechanical efficiency
- They provide a ratio of constant velocity
- Resistant to pollutants and chemicals
- Low upkeep and tidy operation
- Energy-efficient
- Cost-effective because drive enclosures, lubrication, disposal costs, and tensioning devices are not required.
- Ideal for transmission at a low power level
- The power transfer occurs over a shorter distance than with conventional drive belts.
Disadvantages of Timing Belts
- Higher price
Choosing the Proper Timing Belts Supplier
To make sure you have the most constructive outcome when purchasing Timing Belts from a Timing Belts Supplier, it is important to compare at least 4 Companies using our list of Timing Belts manufacturers. Each Timing Belts Supplier has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each Timing Belts company website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each business specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple Timing Belts companies with the same quote.





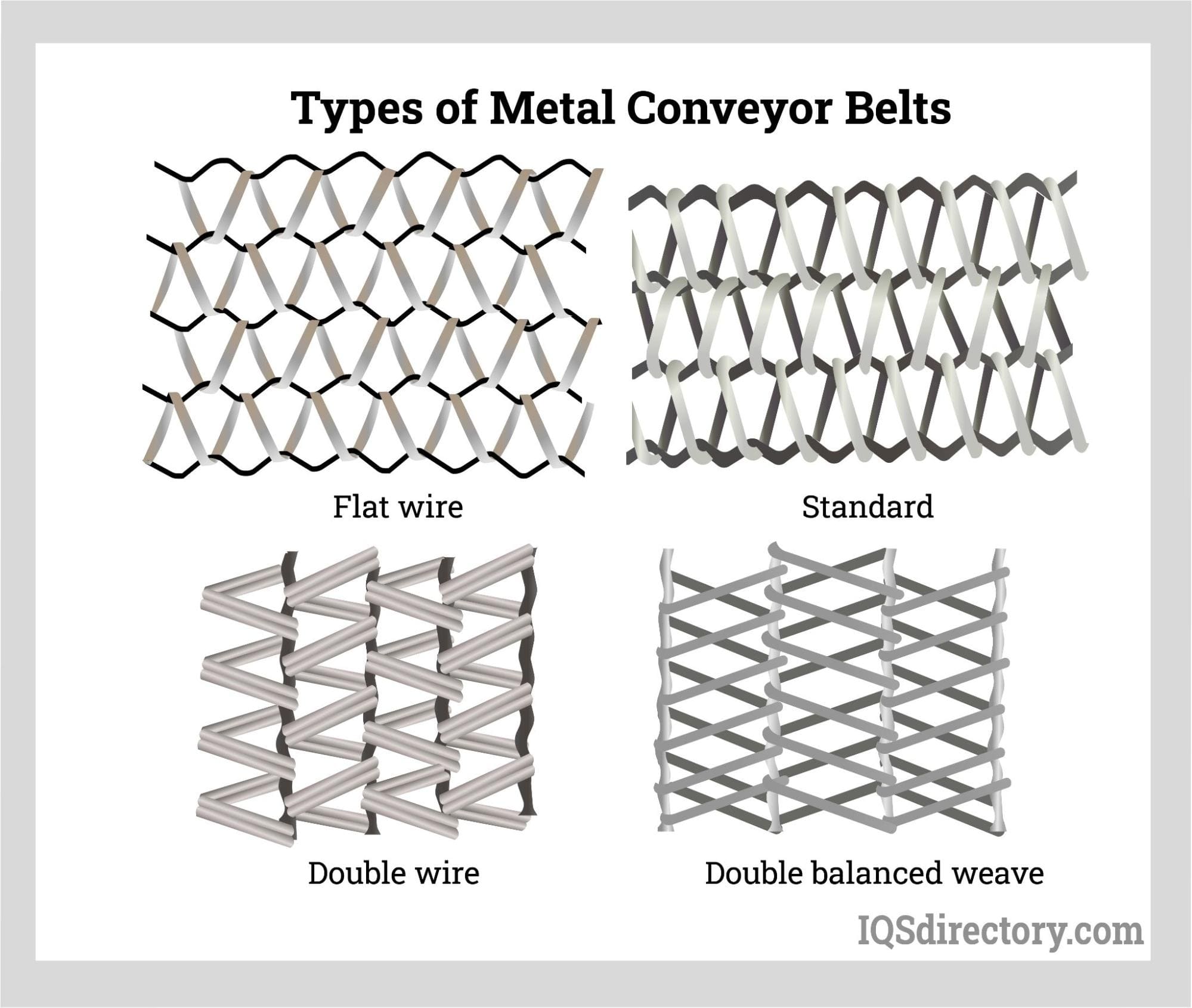

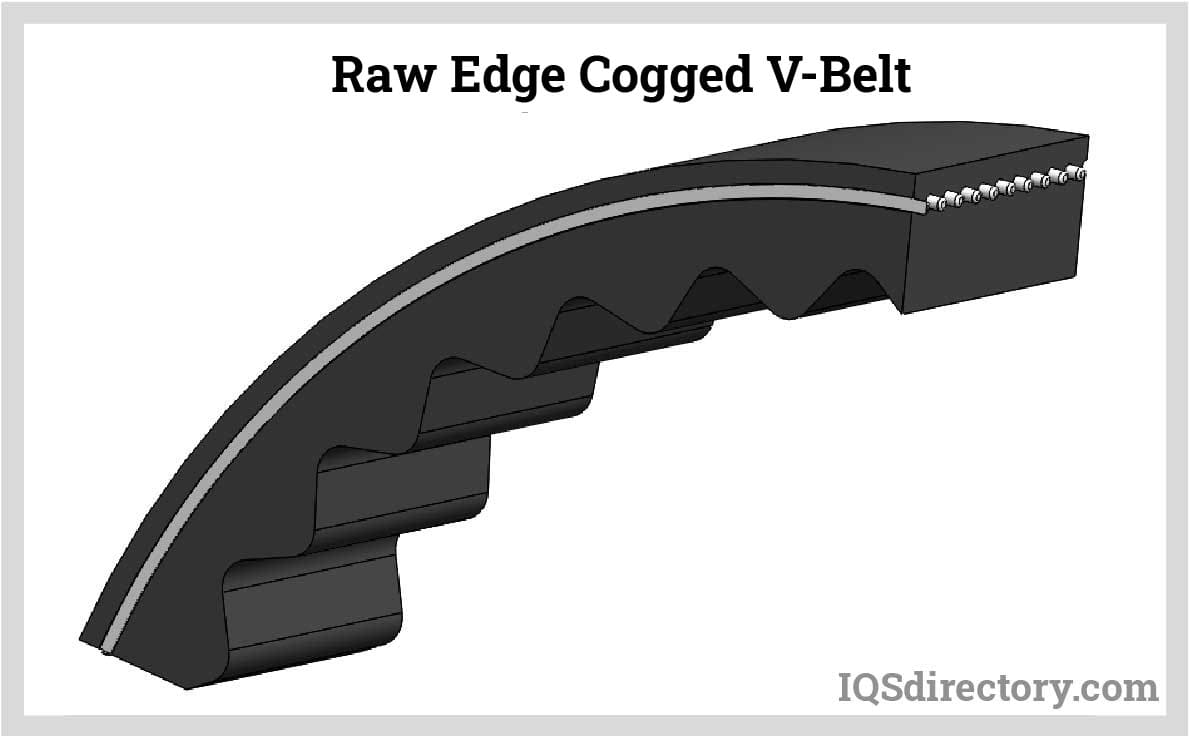




 Conveyor Belting
Conveyor Belting Conveyor Systems
Conveyor Systems Conveyors
Conveyors Hosereels
Hosereels Industrial Lubricants
Industrial Lubricants Lubricators
Lubricators Screw Conveyors
Screw Conveyors Pneumatic Conveyors
Pneumatic Conveyors AGV
AGV Air Pollution Control
Air Pollution Control Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Blowers
Blowers Cranes
Cranes Deburring Machinery
Deburring Machinery Dust Collectors
Dust Collectors Heaters
Heaters Hose Reels
Hose Reels Mezzanines
Mezzanines Modular Buildings
Modular Buildings Storage Racks
Storage Racks Ultrasonic Cleaners
Ultrasonic Cleaners Work Benches
Work Benches